‘International division of labor’ and ‘mass production’ are not always the winning globalization strategy anymore.
Not a few MNCs (Multinational corporations) start to search a new globalization strategy.
Some try to adopt the globalization strategy of GAFA (Google, Amazon, Facebook, and Apple), but they are not sure if it works, yet.
In this column, I would like to explain why the conventional global strategy is getting outdated.
Also, I would like to present an alternative globalization strategy by comparison with the globalization strategy of GAFA.
4 styles of business globalization in 3 eras
Let me start with defining the globalization of business.
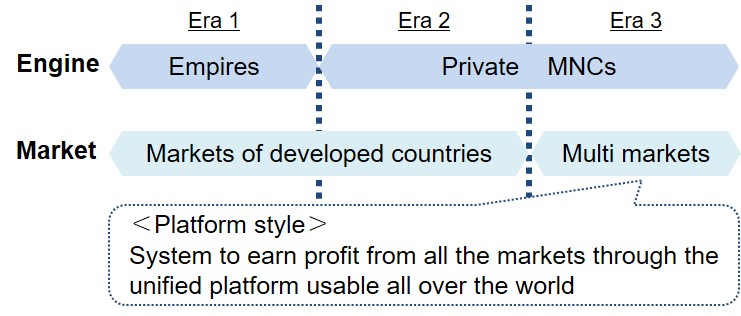
We witnessed and are going to witness 4 styles of business globalization in 3 eras;

The dividers of the eras are the engine of globalization and the type of market.
WW II divided Era 1 and Era 2 by changing the engine from empires to private MNCs, although the market is the same — few mega markets of developed countries.
The globalization of Era 1 is;

Both the Roman Empire and the British Empire are examples of this globalization style.
After the MNCs take over the position of the engine, the globalization becomes;

This style peaked from the latter half of the 20th century to the beginning of the 21st century when Japan, followed by NICEs (Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and South Korea), ASEAN countries, and BRICKs, rose as production countries.
During this time, only developed countries in Western Europe and North America were the mega markets, although Japan market joined in the 1980s.
Many people say that a characteristic of globalization is borderless, but it is wrong.
The globalization of Era 1 is to expand the boarders of the sovereign country.
Also, the globalization of Era 2 is to make the most use of the gap between 2 areas divided by the national borders.
Era 3 starts when the countries in production areas also become the mega markets.
The key point is that the markets do not move from developed countries to emerging countries, but that the number of mega markets increases rapidly.
In Era 2, MNCs could sell few types of products in large quantities to only a few mega markets in developed countries whose preferences and needs are relatively similar.
However, MNCs now needs to prepare a variety of products to satisfy many mega markets whose preference and needs are verified.
To adapt to this situation, GAFA have built one of the globalization styles in Era 3;
GAFA try to make their platform as attractive as possible to increase participants, both sellers/producers and buyers/consumers.
The more sellers/producers join the platform, GAFA can obtain more variety of products which attract more buyers/consumers.
This globalization style fits well with the era of multi mega-markets.
However, the platform has to be so novel to attract participants.
In addition, MNCs have to build the system in which the participants are willing to provide their private data, namely Big Data.
Instead of following GAFA, many MNCs will need to find a globalization style which does not require the Big Data;

This does not merely mean that an MNC has many overseas branches.
Each overseas branch pursues the optimization at its market while cooperating and exchanging information and ideas super frequently with other overseas branches, such as;
- Rolling out a good practice born in Branch A to all other branches
- Creating a new product or a new business model by combining an idea from Branch B and another idea from Branch C
We are given the era, but not the globalization style.
Since the MNCs become the engine of globalization, the globalization style is also the strategy that an individual MNC can choose;
- Keeping the globalization style of Era 2
- Platform Style
- Networking Style
Organization structure
To decide on the strategy, I will explain the choices a bit more from the perspective of organization structure.
The majority of MNCs in Era 2 have deployed a ‘Top-down global organization structure’;
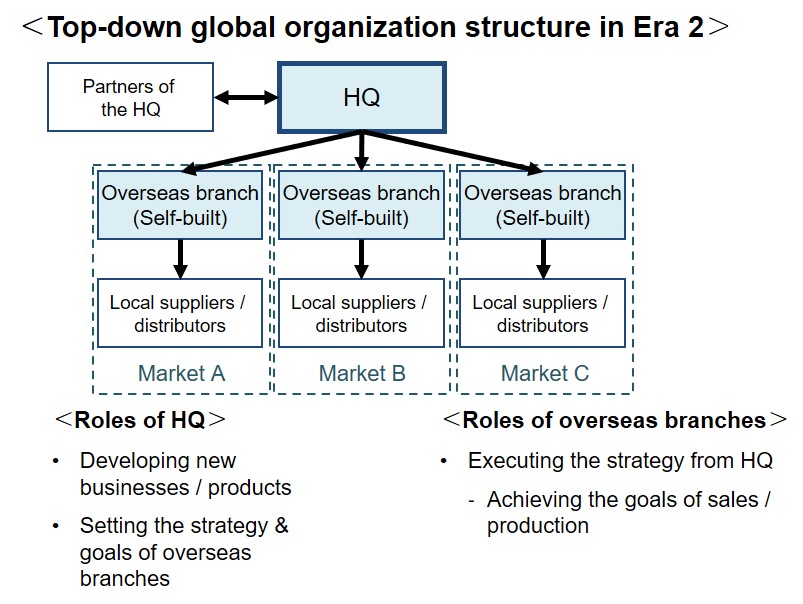
The HQ is usually placed in the biggest market for the MNC, and it makes all the products targeting the market.
The MNC makes a minor change to the products for other markets.
The overseas branches in the other markets focus on sales given the target from the HQ.
The MNC builds its factories in the place where it can expect the lowest cost.
The HQ makes the production plan, and the factories follow the plan.
The key characteristics of this organization structure are;
- Centralization of control to the HQ (Top-down structure)
- Collaboration among overseas branches (International division of labor)
The Platform-style organizations like GAFA evolve ‘Centralization of control to the HQ of the Top-down organization structure;
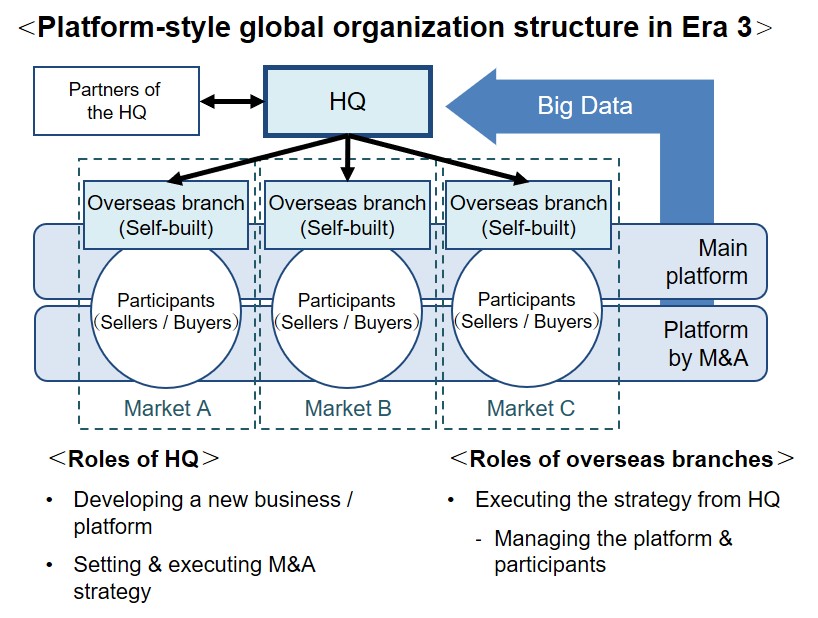
While the global organization in Era 2 manages overseas branches by authority, the Platform-style global organization manages the overseas branches by Big Data automatically collected from its platform.
The HQ develops new businesses, new technologies, annual targets and action plans from the Big Data, and implements them globally.
Another difference from Era 2 is the way to expand globally.
The organization in Era 2 expands its business through long-time contracts with suppliers and distributors.
The Platform-style organization expands by increasing the participants to its platform.
They are usually keen on M&A of other global platforms as the acquired platform can bring more participants.
The example is Google’s acquisition of YouTube.
The roles of overseas branches are not much different from the ones in the Top-down organization structure.
On the other hand, overseas branches will take many more roles in the Networking-style global organization structure;

This structure evolves the other characteristics of the organization of Era 2, — ‘collaboration among overseas branches,’ but it is totally different from ‘international division of labor.’
This organization structure encourages the overseas branches to collaborate with each other without the orders from the HQ.
The overseas branches need to step up from mere executors of the HQ’s strategy to independent-minded business innovators.
The HQ becomes a coordinator to accelerate the collaboration and information sharing among the overseas branches, instead of being a commander as seen in the Top-down organization.
Conclusion
Globalization is not one long history of erasing national borders.
Instead, globalization (especially, of business) is the system (s) of the engine and the markets crossing national borders, and the style of globalization changes over times.
Since Era 2 when MNCs become the engine, the styles mean the strategies which the MNCs can choose.
However, not many MNCs can follow the Platform-style without Big Data.
Nor, in the era of multi mega-markets, not many MNCs can grow globally in the long run with the Top-down organization structure.
So, in the next column, I would like to explain how to manage Networking-style global organization, and how to develop talents fitting with this type of organization.

© Kuroshio HR Consulting, Ltd. 2020
