To survive multi mega-market world, I recommend the Networking-style globalization strategy for most MNCs in the last column;

In today’s column, I would like to discuss how to manage the Networking-style global organization, and how to develop talents fitting with this type of organization.
Film competition, not track race
In a Top-down global organization, the HQ manages its overseas branches like a track race.
The HQ sets the goal (sales and productivity) and regulations, and the overseas branches try to reach the goal with a similar methodology.
On the other hand, the Networking-style global organization should manage the overseas branches like a film competition.
To win the award, filmmakers can make whichever drama, comedy, SF, or documentary as long as they think it is the best.
Likewise, in the Networking-style global organization, the overseas branches appeal to the HQ and other branches with a variety of value-added practices.
The award-winning value-added practices should not be limited to sales and productivity.
They include developing a new product able to roll out to other branches, finding good local partners to share with other branches, and developing talents who can be the future executives of the MNC.
The award is an investment from the HQ.
The more contributions a branch makes (or is going to make) in various ways, the more the HQ invests in the branch.
In this sense, this is not management but encouragement.
The HQ should stimulate its overseas branches by sharing a good value-added practice from one branch to the other branches as quickly as possible.
For winning the award
To gain investment more, an overseas branch needs to know its positioning among other branches, in the first place.
The key criteria to know the positioning are the capabilities of the branch and market attractiveness the branch is in charge of;
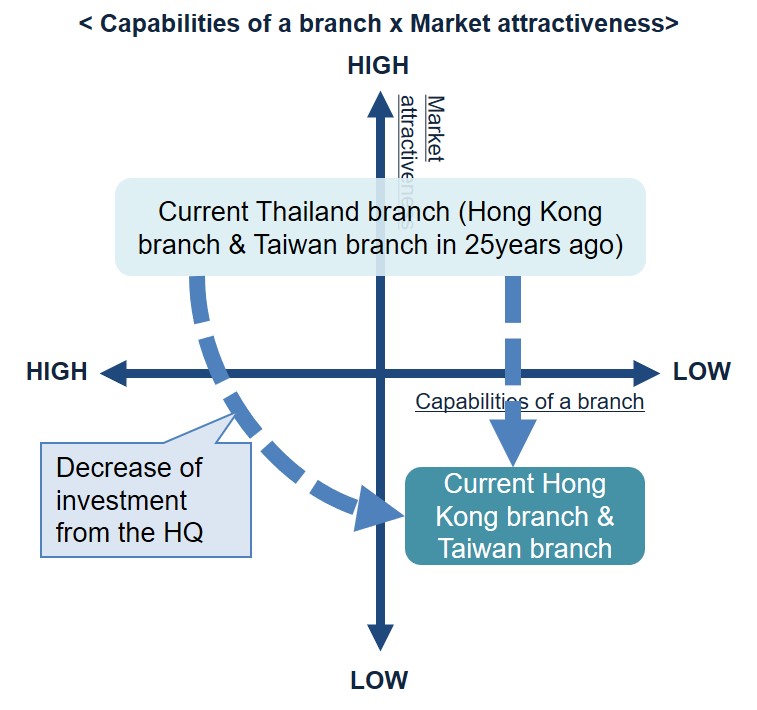
As an example, let me describe the positioning of a Hong Kong, a Taiwan, and a Thailand branch of a Japanese MNC;
The HQ invests a lot in its Thailand branch, as Thailand is a good growing market with relatively low labor costs and political stability in these several years.
Japanese MNCs saw Hong Kong and Taiwan in a similar situation in 25 years ago.
However, the HQ has decreased investment in the Hong Kong branch and the Taiwan branch for these 25 years along with the slowdown of the market growth and the higher labor cost.
The less the HQ invests, the weaker the branches become.
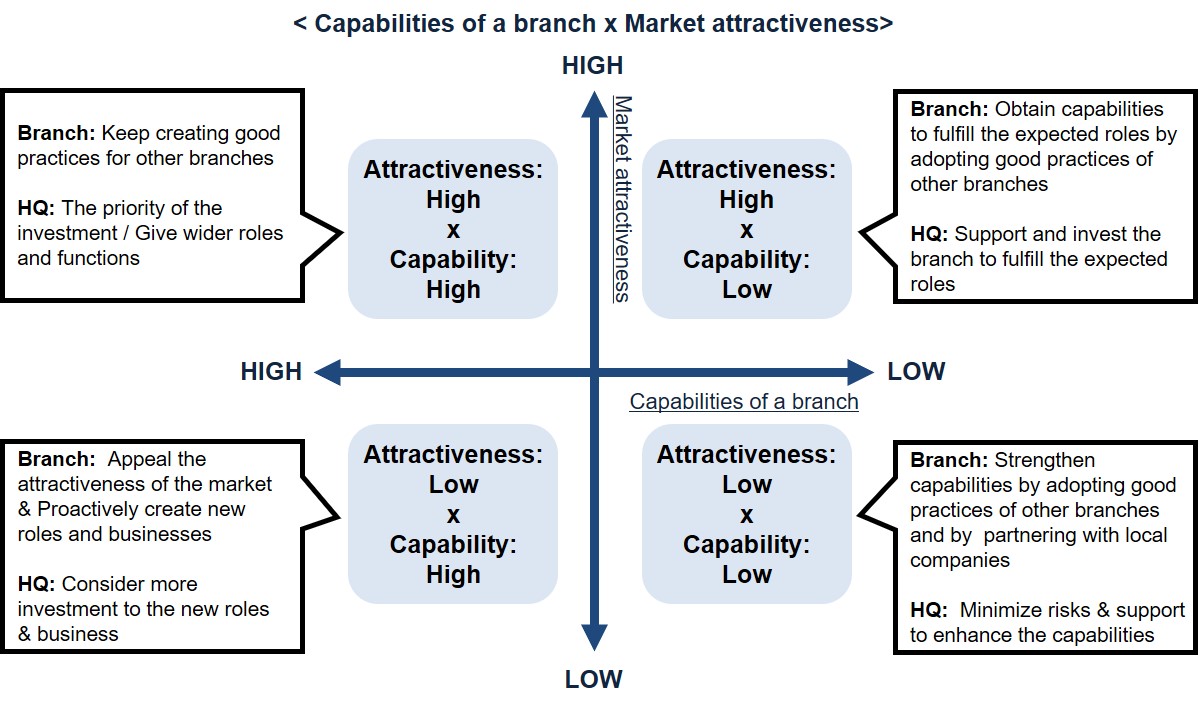
By understanding the positioning as shown in the example, the branches need to build their strategies.
The Thailand branch should find a strategy to keep the current market attractiveness while gaining higher capabilities.
The Hong Kong branch and the Taiwan branch are in a more difficult situation as one company cannot change the slow-down of the economy or the high labor cost.
However, a good thing about ‘Film Competition’ is that the HQ does not focus only on sales or on productivity for giving the ’award’.
Hong Kong and Taiwan have many good local companies with attractive technologies and products.
By partnering with them, the branches can strengthen their capabilities.
In addition, sharing the local partners with other branches will be a good value-added action as well as a good display of the market attractiveness.
Also, Hong Kong and Taiwan are rich with talents who have good education and multicultural experiences.
This can be another market attractiveness if the branches hire and develop the talents to contribute to the MNC as a whole.
The picture below shows the general direction of a branch and the HQ in each positioning;
Inviting the members of overseas branches to ‘Film Competition’
Innovating value-added practices requires new ideas, the guts to challenge new things, and the eagerness to grow.
In other words, the members of an overseas branch have to be highly motivated toward ‘Film Competition.’
The order and numerical targets made by the HQ do not work well for it, especially when the HQ gives ‘a tiny role’ to the branch in the HQ’s ‘script.’
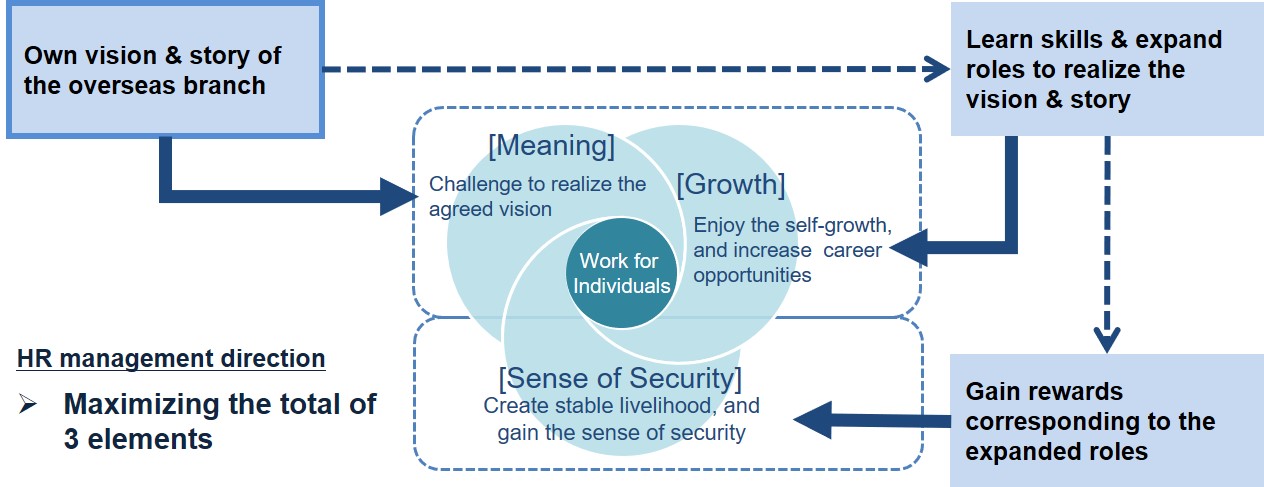
To motivate themselves, the members need their own vision and story of their branch, in which they can play the ‘main roles’.
In addition, the members themselves should write and agree to the vision and story by themselves based on the positioning of their branch.
The picture below is a part of our consulting approach, showing the 3 basic elements that people expect from their work;
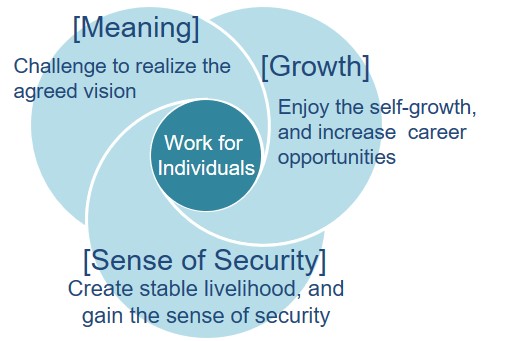
The bigger the total of 3 elements is, the higher the work motivates the member, although the proportion of 3 elements will change by each member or by his/her life stage.
If they are communicated well, the own vision and story affect the elements as described in the picture below;
Connecting overseas branches
Once the overseas branches are ready to innovate value-added practices, the Networking-style global organization should now accelerate communication among the overseas branches.
For this purpose, the organization needs to dissolve;
- Slow and complex communication flows always bypassing the HQ
- Top-down management style
The key solution is placing HQ functions at overseas branches.
In each function or line of business, each overseas branch assigns one member to a global committee in which the members discuss, adjust, and solve the organization-wide problems and opportunities.
The global committees function as HQ.
The members should be Geographical T-shaped talents;
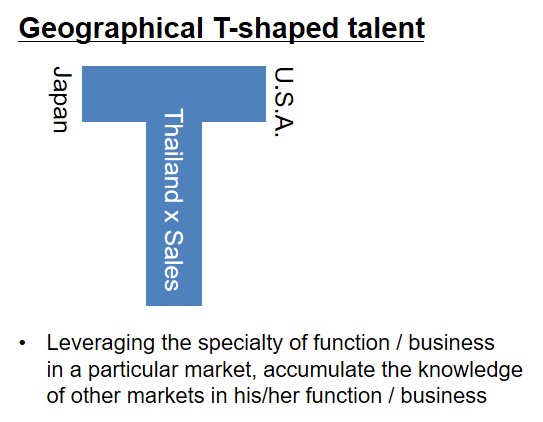
The members do not have to gather at one location.
Instead, they stay at their own overseas branches in order to keep updating the market information, new practices, and ideas of their branches, and to deliver them to other global committee members as quickly as possible.
Thus, they take care of their function / business activities in the branches with Functional / Business T-shaped talents;
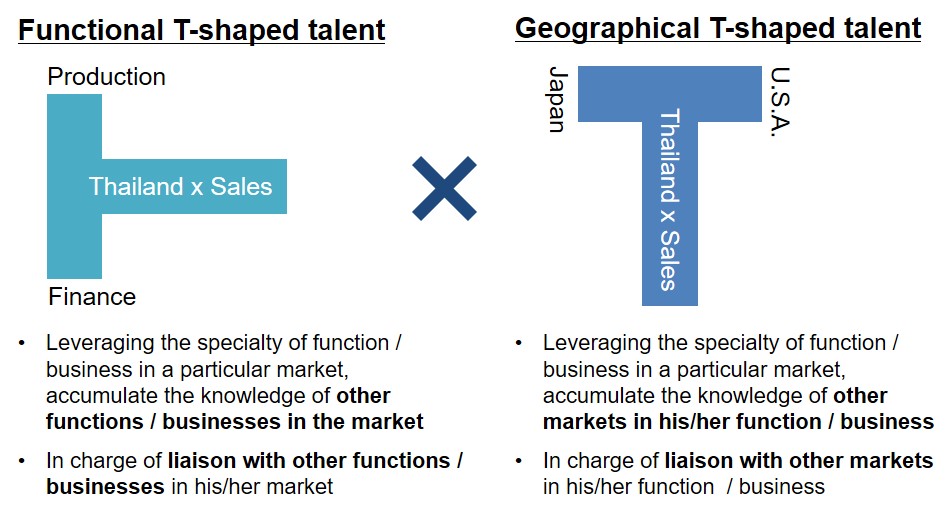
Usually, either of the two is the function / business head of a branch and the other is the vice function / business head.
An MNC does not have to place the vice function heads if the function heads have the capabilities of both Functional T-shaped talent and Geographical T-shaped talent.
However, not many MNCs can afford such highly capable talents enough to place all the function head positions of all the branches.
The whole picture is like this;

In a branch, a Geographical T-shaped talent shares the discussion contents in the Global Committee to a Functional / Business T-shaped talent, and discuss the best actions the branch can choose.
In this way, each function / business unit of overseas branches can make the best decisions by taking into account the other overseas branches’ views, plans, and actions.
Under the function / business head and the vice head, the members of the function / business unit execute both local tasks and tasks of the Global Committee.
By doing so, the members of the unit learn to balance the local market view and the total optimization view, from their early career stage.
Also, they will need to work with the members of other overseas branches for the tasks of the Global Committee.
This will expand their overseas network, which will be a benefit, especially for future Geographical T-shaped talents.
While the Global Committees and the overseas branches partly work as the HQ, the original HQ focuses on setting & executing investment policies for overseas branches, and financing for the investment.
Developing talents
For the members of overseas branches, either a Geographical T-shaped talent or a Functional / Business T-shaped will be their initial career goal.
Thus, their career development paths in the organization are like this;
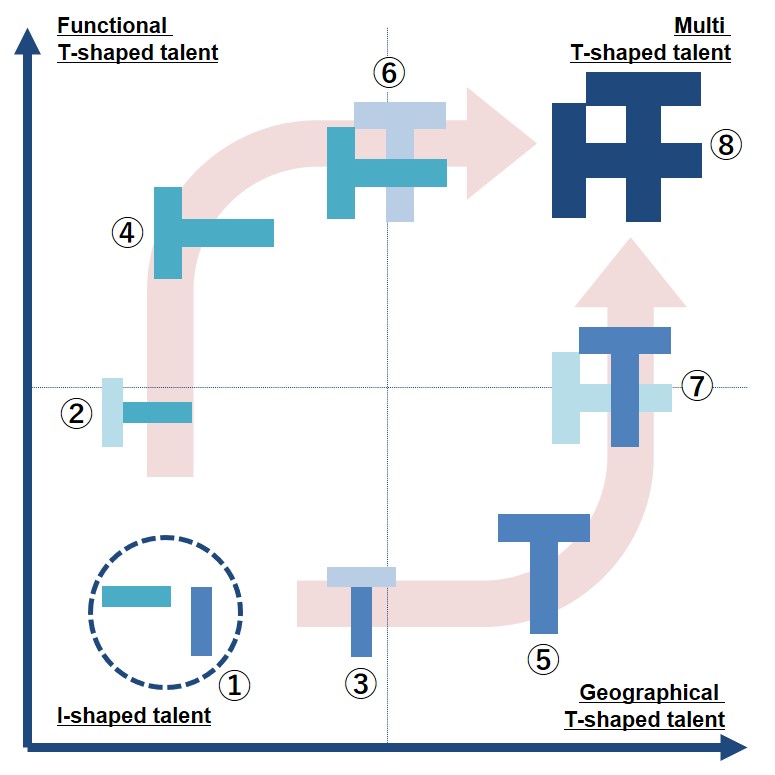
① to ⑧ are milestones of career development in the organization.
The following chart shows the skill level and the expected positions of the milestones;

In the Top-down global organization, the career development paths are usually separated between the HQ and the overseas branches.
Or at least, the members of overseas branches do not have many chances to pursue career development in the HQ.
On the other hand, in the Networking-style global organization, the overseas members can pursue both the local market career path and the HQ function career path while staying in their market.
Attracting and retaining talents
The capability to attract and retain talents depends on the attractiveness of the organization and the wideness of the talent network.
If managed properly, the overseas branches of the Networking-style global organization have both of them;
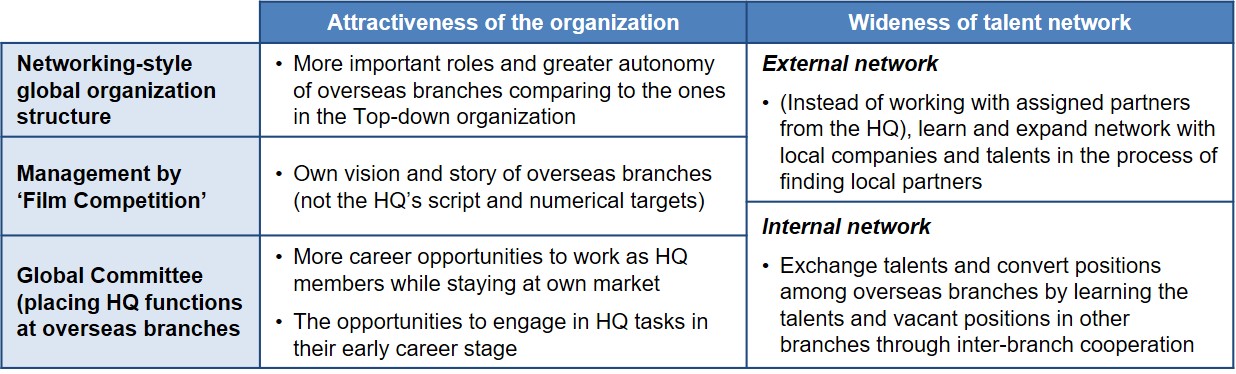
I believe the attractiveness and the wideness of the talent network can hold out against the novelty and the strong brand of GAFA-like MNCs.
Conclusion
The transformation to the Networking-style global organization is not only the change of the organization structure.
The changes include;
- More autonomy of overseas branches
- Deeper and more frequent communication and cooperation among overseas branches
- Seamless exchange of market insights and global optimization view
Overall, the transformation requires both a change of mindset and the daily actions of overseas members.
The members need to become more independent, flexible, willing to initiate new things, and more responsible for the future of their branches.
Some may feel it is a burden.
However, if the MNC can properly support the members in development, most of them will enjoy their work much more in the Networking-style global organization.
© Kuroshio HR Consulting, Ltd. 2020
